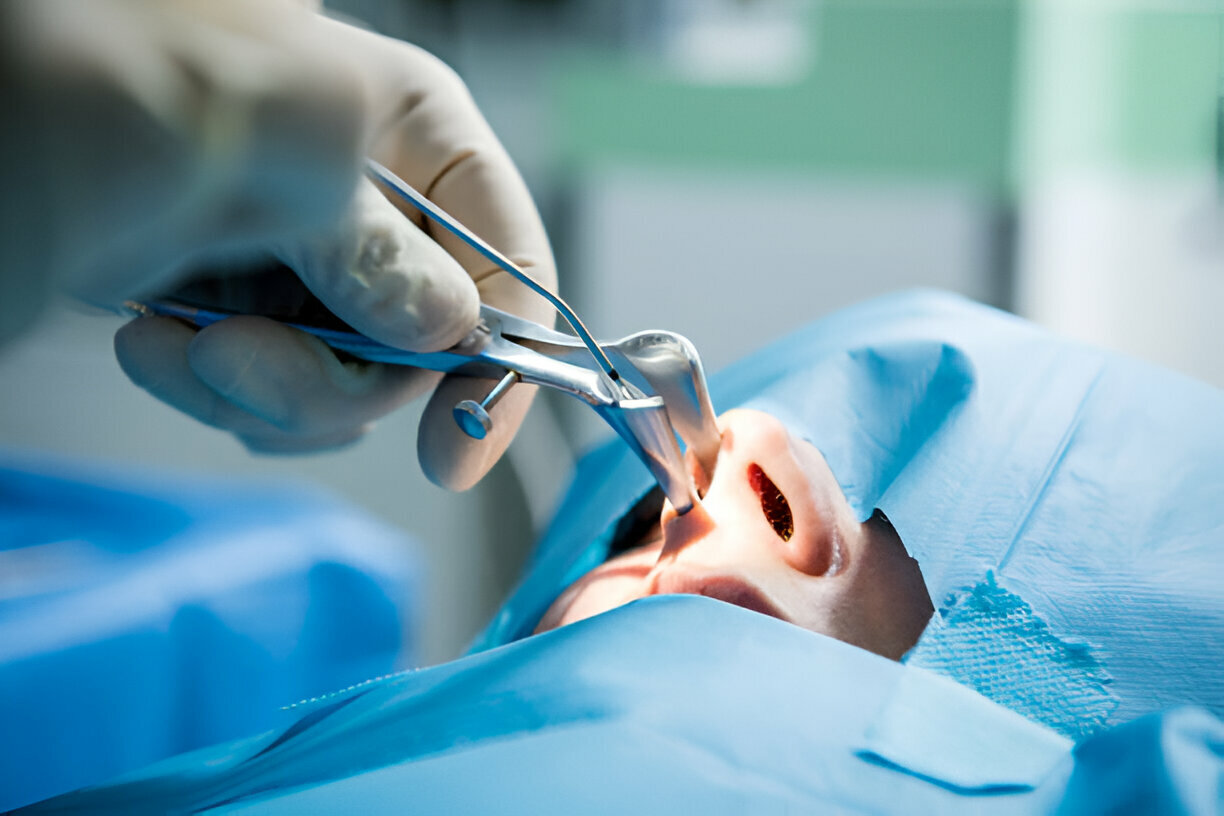
COBLATION SURGERIES
Coblation (derived from “controlled ablation”) is a surgical technique that uses radiofrequency energy combined with saline to create a plasma field that can precisely remove soft tissue with minimal damage to surrounding areas. This technology is used in various medical fields, including otolaryngology (ENT), orthopedics, and spine surgery, to treat conditions ranging from tonsil hypertrophy to chronic sinusitis.
Principles of Coblation
- Radiofrequency Energy: Coblation uses low-temperature radiofrequency energy to excite the saline, creating a plasma field.
- Controlled Ablation: The plasma field dissolves molecular bonds within the soft tissue, allowing precise and controlled tissue removal.
- Minimal Thermal Damage: The technique operates at lower temperatures than traditional electrocautery, reducing collateral damage and promoting faster healing.
Common Indications
- Tonsillectomy (removal of the tonsils)
- Adenoidectomy (removal of the adenoids)
- Turbinate reduction (to improve nasal airflow)
- Treatment of snoring and obstructive sleep apnea
- Removal of nasal polyps
- Sinus surgeries
- Soft tissue procedures in other medical fields

